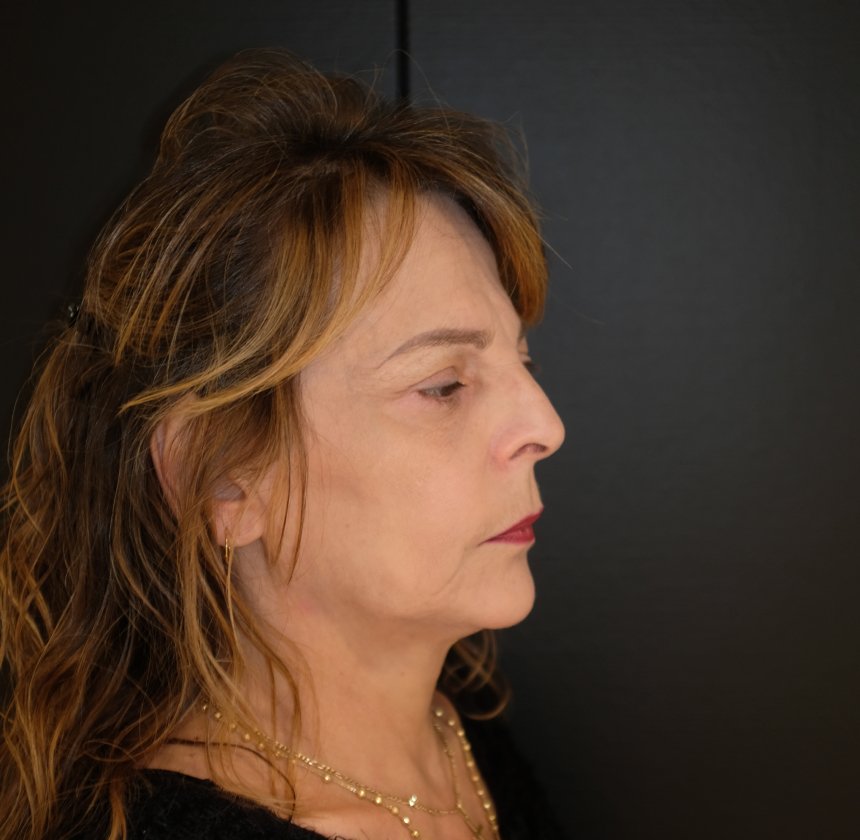
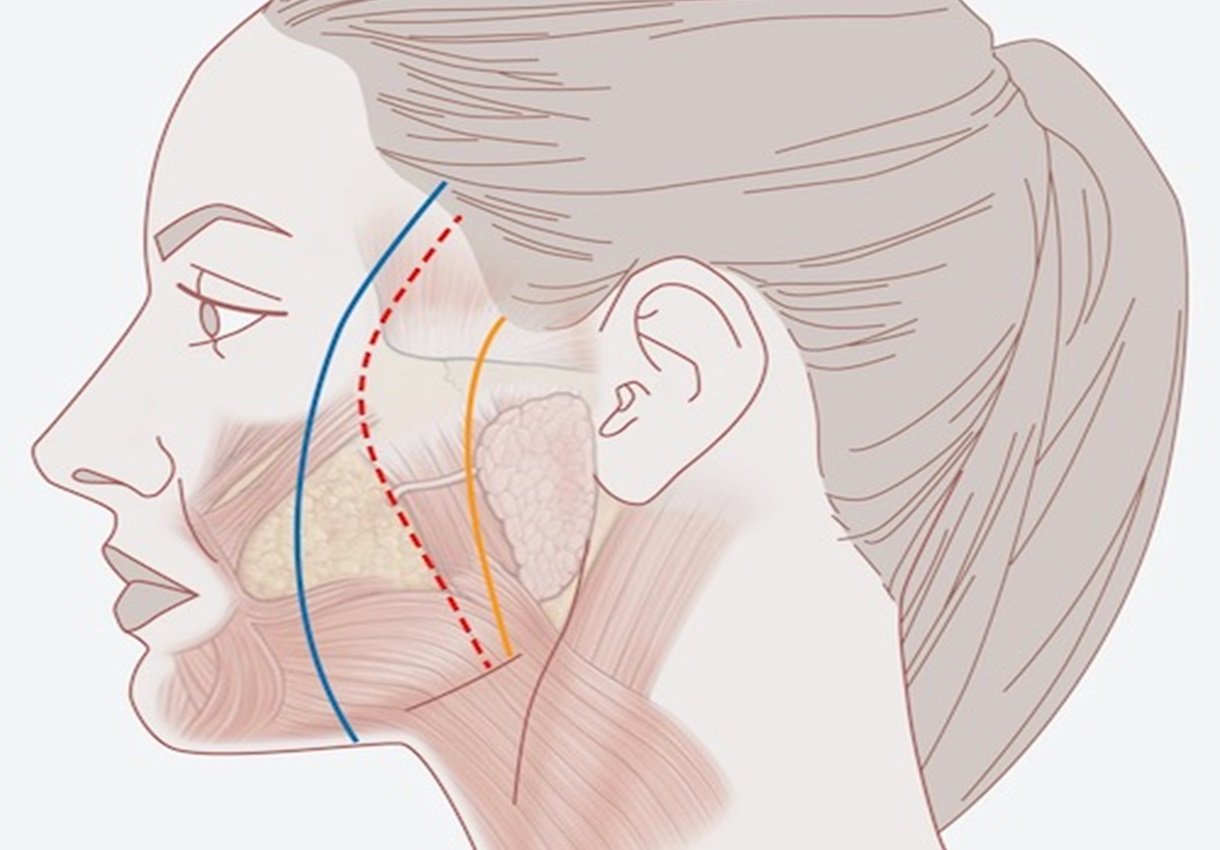
The traditional techniques of facelifts by primarily skin removal have a short duration of effect and poor wound healing with visible scarring. The problem is the high tension during wound healing. Studies show that with the so-called SMAS technique (= superficial musculoaponeurotic system), in which the midface is also treated, a more natural result with a long-term effect can be achieved.

How does the "High SMAS technique" work?
When the SMAS flap is tightened below the zygomatic arch, the effect on the midface and eye region is missing. Only the lower half of the cheek is lifted. With the “High SMAS technique” the SMAS flap is lifted higher, above the zygomatic arch. This allows simultaneous tightening of the midface, cheek area and jawline.
Skin flap dissections:
A) Minimal B) Limited C) Extended
What are the benefits of autologous fat treatment in combination with the “High SMAS technique”?
The autologous fat treatment (“microfat”) is very often combined with the “High SMAS technique” to restore the loss of volume in the midface and eye region. The nanofat treatment can also improve skin quality.
When is autologous fat treatment used?
As a rule, the autologous fat treatment is carried out before the facelift.
What are the risks for nerve injuries?
There were initial concerns that this technique posed an increased risk of injury to the so-called frontal branch of the facial nerve (ramus frontalis of the facial nerve). However, anatomical studies have shown that the “High SMAS technique” is safe with respect to the frontal branch.
What is the “lamellar” preparation technique?
There are different preparation techniques to lift the SMAS. The SMAS can be lifted and tightened together with the skin (so-called “composite” preparation technique). However, the skin and the SMAS age differently and the tightening of the two layers should be done in different directions. With the “lamellar” preparation technique, the skin and SMAS are approached and tightened separately, and the result is more natural.
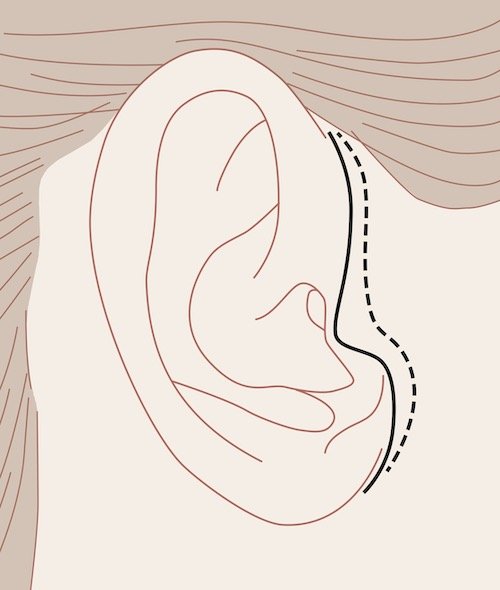
How is the incision in front of the ear?
The incision in front of the ear can be made intratragal/posttragal (= behind the tragus (tragus = cartilage attachment of the outer pinna)) or pretragal (= in front of the tragus). The intratragal/posttragal incision is performed more frequently as the scar is not visible.
The pretragal incision is more visible and can be used if the skin color between the cheek area and the tragus is different or if the tragus cartilage is very prominent.
Can a neck lift be performed at the same time as the “High SMAS technique”?
A simultaneous face lift and neck lift is almost always the best treatment to achieve a natural and harmonious result. It is unusual for there to be only excess skin on the face without excess skin in the neck region. A neck lift often requires an additional incision under the chin (called a submental incision).
What kind of anaesthesia is necessary?
As a rule, the procedure is performed under deep sedation (so-called twilight sleep) with a laryngeal mask. This type of anesthesia is gentler than the endotracheal tube and allows spontaneous breathing. However, there is always a consultation with the anesthetist before the operation.
What do I need to bear in mind after the operation?
After the procedure you should lie flat without a pillow. You should refrain from salty, sour, hard food or alcohol for 2 weeks. Showering with shampoo is allowed after 3 days. Stitches are removed after 5 – 7 days. After about 4 weeks, unrestricted sporting activity is possible. The scar must be protected with a sunscreen SPF 50 for up to one year or treated regularly with a greasy ointment.